CSS
various things I pick up along the way.
Z-Index and Stacking Contexts
When you give an element a z-index, that value is only compared against other elements in the same context. By default, an HTML document only has one context. Here's an example of one way to create a context:
.some-element {
position: relative;
z-index: 1;
}
Other ways to create stacking contexts:
- set opacity to less that 1
- set position to fixed or sticky
- apply a mix-blend-mode other than normal
- add a z-index to a child inside a display:flex or display:grid container
- using transform, filter, clip-path, or perspective
- explicitly with isolation: isolate
More on this: What the heck, z-index? - Josh Comeau
Animation
see CSS Animation
Flexbox
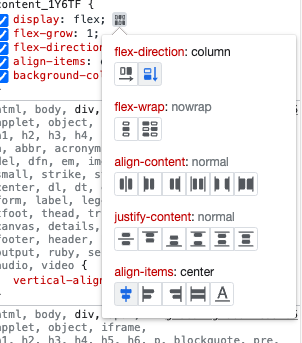
Flexbox help in Chrome Dev Tools
click the gray box next to a flex property to inspect the different properties: